When choosing an embedded computers, there are several factors to consider in order to find the best option for your needs. Below are some tips on how to select the right embedded computer for your specific requirements.
Decide on the required features and specifications
When shopping for an embedded computer, you first need to decide what features and specifications are necessary. This will help you narrow down your options and find the best computer for your needs. Some factors to consider include processing power, memory, operating system, input/output ports, and size.
Consider the environment where the computer will be used
Embedded computers are used in a wide variety of environments, so it’s important to consider the conditions under which it will be operated. For example, if it will be used in a dusty or wet environment, you’ll need a model that is specifically designed for those conditions.
Choose the right form factor
Embedded computers come in a variety of form factors, from small modules that can be integrated into other devices to large rack-mounted systems. You need to choose the form factor that best suits the intended application. For example, if portability is important, you’ll want a smaller form factor; if performance is critical, then you’ll need a system with more powerful hardware.
Compare prices and reviews
Once you’ve determined the required features and specifications, it’s time to start shopping around and compare prices. Be sure to read reviews from actual users to get an idea of how well the computer performs in real-world scenarios.
5 reasons to use embedded computers in your next project
1. Embedded computers are more power efficient than traditional desktop computers, meaning they can run longer on a battery or use a lower-wattage power supply.
2. Embedded computers are smaller and lighter than traditional desktop computers, making them easier to transport and use in tight spaces.
3. Embedded computers typically have a longer lifespan than traditional desktop computers, making them a more cost-effective choice in the long run.
4. Embedded computers are often more ruggedized than traditional desktop computers, making them better suited for harsh environments or industrial applications.
5. Embedded computers typically come with a variety of built-in features that are not available on traditional desktop computers, such as timers, counters, digital inputs/outputs, and communication interfaces.
How to choose the right embedded computer for your needs
Embedded computers come in all shapes and sizes, and choosing the right one for your needs can be daunting. Here are some tips to help you make the right decision:
Decide what you want the embedded computer to do.
Are you using it to control a machine or process? Are you using it as a data acquisition system? Or are you using it for some other purpose? Knowing what the embedded computer will be used for is the first step in choosing the right one.
Consider the environment where the embedded computer will be used.
Is it going to be in a dusty or wet environment? Is it going to be exposed to extreme temperatures? The environment can help determine which embedded computer is best suited for your needs.
Choose an embedded computer that fits your budget.
Not all embedded computers are created equal, and some will be more expensive than others. Choose the one that fits your budget and meets your needs.
Do your research.
There are many different types of embedded computers available, so do your research before making a decision. There are plenty of online resources that can help you make an informed choice.
What are the types of embedded computers?
There are a few different types of embedded computers: single-board computers, system-on-modules, and COM Express.
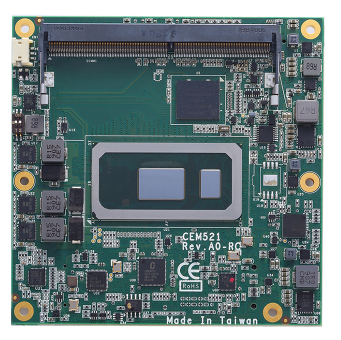
Single-board computers are designed to do one thing and one thing only, which is why they’re often used in industrial or automotive applications. They’re typically small and low-power, making them ideal for tight spaces.CEM521 – 8th gen i core/celeron COM Express Type 6 Compact Module with 8th Gen Intel® Core™ & Celeron® Processor
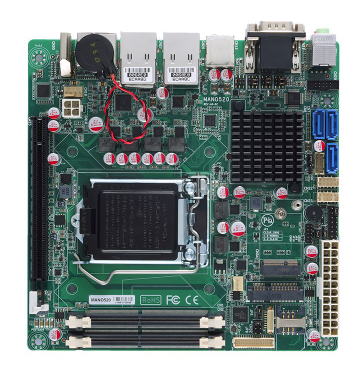
Mini itx motherboards are a little more versatile; they offer more features and functionality than single-board computers, but they’re still relatively compact and power-efficient. They’re often used in medical and military applications MANO520 – 9th gen LGA1151 CPU Mini-ITX SBC with LGA1151 9th/8th Gen Intel® Core™ i7/i5/i3 Processor, Dual DisplayPort++, HDMI, LVDS, USB 3.0, mSATA, M.2 and Dual GbE LAN.
Lastly, COM Express modules are the most powerful and versatile of the three types. They offer the same features as system-on-modules but with even greater processing power and memory capacity. They’re commonly used in industrial applications.
Now that you know the different types of embedded computers, let’s take a look at some of the factors you should consider when choosing one.
Why embedded systems are perfect for industrial applications
Industrial Computing is small, lightweight computers that are perfect for industrial applications. They are designed to be efficient and reliable, and they can be used for a variety of tasks, including data collection, machine control, and process automation.
AIEdge-X300 Industrial AI Computing System
One of the benefits of using the AIEdge-X300 Industrial AI Computing System in industrial applications is that they are typically very rugged and can withstand harsh environments. They also have a long lifespan, which makes them a cost-effective option in the long run. Additionally, embedded systems can be easily customized to meet the specific needs of your business.
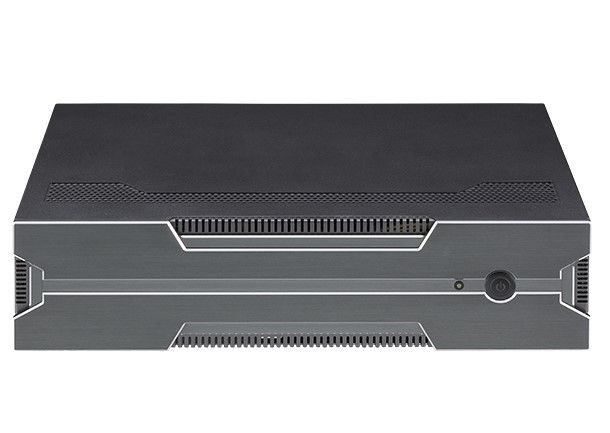

If you’re looking for a reliable and efficient computer system for your industrial application, then embedded systems are a great option. Contact us today to learn more about our embedded systems and how they can benefit your business.
What are the benefits of using an embedded computer?
An embedded computer system is a computer system that has been designed for a specific task or set of tasks. Unlike desktop or laptop computers, which are general-purpose devices that can be used for a wide variety of tasks, embedded systems are typically dedicated to a single function.
There are many benefits to using an embedded computer system. First, embedded systems are often smaller and more compact than traditional desktop or laptop computers, making them ideal for use in tight spaces. They also consume less power, making them more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Second, embedded systems are often more reliable and stable than traditional desktop or laptop computers. This is because they have been specifically designed for the task at hand, and therefore tend to have fewer glitches and errors.
Finally, embedded systems can be much cheaper than traditional desktop or laptop computers. This is because they typically do not include the same level of features and functionality as a standard computer.